What is the Difference between Tendonitis and Tendonosis

What’s the difference between tendonitis and tendonosis?
Many people experience tendonitis at some point in their life. Tendonitis often appears in the elbow, knee, ankle, shoulder or hip as the result of inflammation of the tendon cells (tenocytes) and can materialize and worsen gradually over time or can come on suddenly with severe pain. While tendonitis is fairly common, less people are familiar with the term tendonosis.
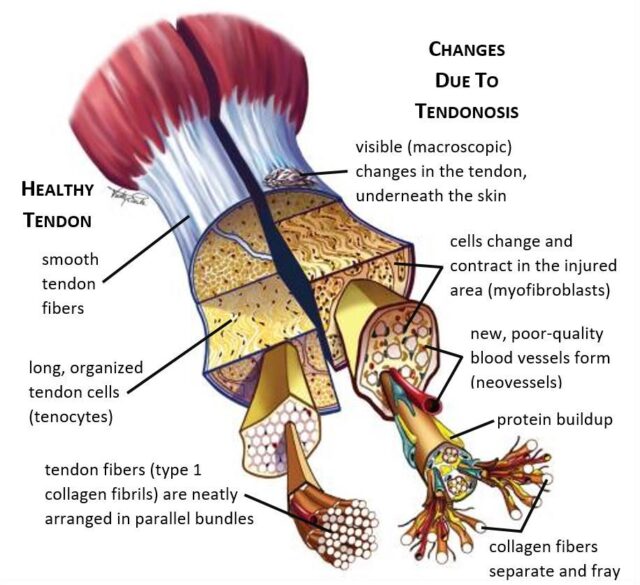
Tendonosis is a chronic condition where inflammatory cells are replaced with degenerative cells. Because tendonosis is a degenerative condition, the interventions and treatments recommended will be different.
Why understanding the difference is important
The difference between tendonitis and tendonosis is the level or progressive damage to the tendon. While tendonitis is the result of inflammation, tendonosis is a chronic condition in which the tendon is damaged resulting in disorganized fibers and a hard, thickened, scarred or rubbery appearance. While tendonitis often results from overuse or sports injuries, tendonosis is a chronic condition that often requires different and more intensive treatment. Research shows that what is often thought to be tendonitis is often actually tendonosis, so it’s important to see the right medical professional for a proper diagnosis.
An orthopaedic doctor or surgeon will often use an ultrasound to determine whether pain is caused by inflammation or degenerative changes in the tendon. It is important to recognize the difference to ensure it can be treated early and treated properly. Seeing a professional orthopedic doctor can ensure that temporary foot pain does not turn into a lifelong foot injury that could require surgery.
Common Causes of Tendon Pain
Tendon pain isn’t something that only serious athletes experience. Our daily routines can cause damage to our tendons and may cause ligament, foot, or ankle swelling and other pain.
These activities can include:
- Vigorous exercise or playing sports without enough rest
- Performing repetitive work tasks which lead to chronic conditions limiting people’s ability to work (i.e. athletes, carpenters, painters)
- Tendonitis left untreated
- Poor posture
- Wearing poor-fit or improper footwear
There are several tendons in your body that can cause complications to include:
- Extensor Tendon (Tennis Elbow)
- Rotator Cuff Tendons (shoulder)
- Patellar Tendons also known as Jumper’s Knee (knee)
- Gluteal Tendons (hip)
- Achilles Tendon (foot/heel)
What types of treatment are available?
Your doctor will determine the best treatment plan for tendonitis or tendonosis based on your specific diagnoses, however you can expect that the plan will include some of the following treatments:
Tendonitis Treatment
The goals of tendonitis treatment are to reduce your pain and reduce the inflammation.
- Rest and avoid inflicting pain on the painful area in a repetitive motion (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation)
- Anti-inflammatory over the counter (OTC) medication such as ibuprofen or naproxen
- Straps or Braces
- Corticosteroid injections
- Custom Orthotics
- Physical Therapy
- Dry needling or Ultrasonic treatments
Tendonosis Treatment
The goals of tendonosis treatment are to break the cycle of injury; reduce ground substance, pathologic vascularization, and the resulting tendon thickening. Additionally, treatment aims to optimize collagen production and maturation so that the tendon can regain its tensile strength. The treatment plan may include some of the following techniques.
- Physical Therapy
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections from your own blood to stimulate a healing response
- Anti-inflammatory medication (natural and prescription)
- Immobilization
- Custom Orthotics
Recovery
Tendonitis should be diagnosed early by an orthopaedic doctor before tendonosis occurs. If treated early, it can heal successfully in approximately six weeks . If you are experiencing any pain or discomfort, schedule an appointment at Central Texas Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Center.

